Summarization
The world’s biggest economy, United states may be heading into a recession in approximately 12-18 months. But, the recent factors indicate a mild and prolonged recession with fewer tools available with Fed and Fiscal policymaker. It’s important to know what is recession to be prepared for it and allocate your financial portfolio accordingly.
| Indicator | Strength |
| Real Retail Sales | Weak |
| 10 year- 3-month Government yield curve | Weak |
| Unemployment gap and hourly hour worked (YoY) | Neutral |
| Real Fed Rate and leading indicator | Neutral (Deteriorating) |
| Monetary tools | Neutral |
| Fiscal Policy strength | Weak |
| Housing Market | Strong |
Definition of Recession
Two consecutive quarters of decline in economic growth measured by a country’s Gross domestic product is consider Recession.
Illustration of recent recession:
Housing Bubble in 2008The Financial crisis in 2008 is still the worst crisis since the great depression in 1930s. The leading cause was the bubble in housing market, an inferior asset quality which lead to subprime crisis
Dot.com bubble in Technology companies
The technology bubble experienced higher technology company valuation. The Dot.com bubble in 2001 had one of the worst bear markets as stock plummet more than 50% in technology companies.
The below graph summarizes the conclusion that we are approaching a recession; and possibly a mild recession relative to the recent crisis in 2008.
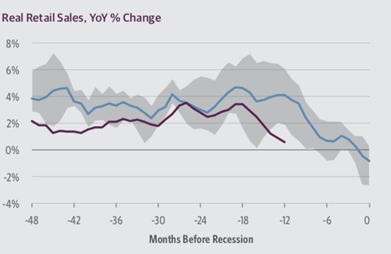
Real Retail Sales
The Real retail sales growth have fall from more than 3% to below 1% in 6 months. This is below the average sales 12 months prior to recession and also less than the lower bound of real retail sales relative to previous recession cycle. Consumer spending is a major proportion of economic activity in United States and retail sales having a significant impact on the consumer spending has seen a decrease recently. This indicates a slowdown in United States.
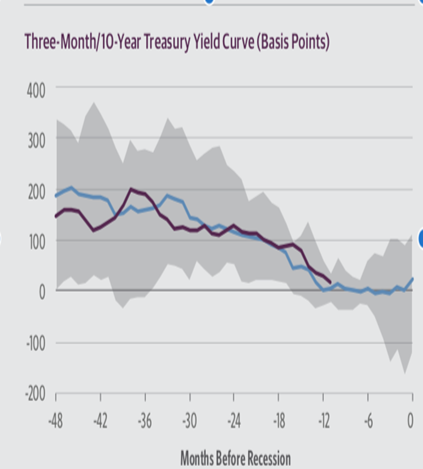
10 Year- 3-month Government Yield Curve.
The inverted 10 year- 3-month Government yield curve has been one of the trusted sources to predict recession. It explicitly depicts the relationship and yield for investing in 10-year treasury bond, the most liquid Government bond, and the 3-month yield, observed in short-term lending/money market as the cost of short-term borrowing rate by the Treasury.
Empirical evidence shows that the inverted 10 year – 3 months has served as an indicator for recession. The recent inversion indicates that the bond yields at the long-end of the curve is yielding less than the short-end of the yield curve. This implies that the long-end of the yield curve is not compensating the investor with term maturity premium but the market is comfortable holding the long end as it sees the approaching recession and subsequent rate cuts. This has increased the probability of recession in future.
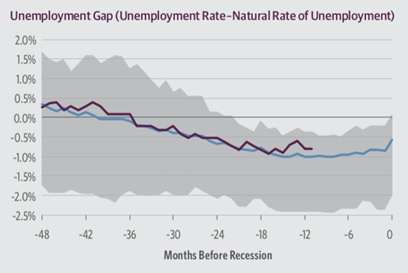
Unemployment Gap
The unemployment gap, unemployment rate adjusted for natural rate of unemployment, is negative but wider relative to average unemployment gap in prior cycle. This gives the fiscal policy makers some tools to grow economic activity by increasing employment to support economy as long as such jobs can be created. The Gross domestic product (GDP) growth and potential output has direct relation with increase in labor force and labor force participation.
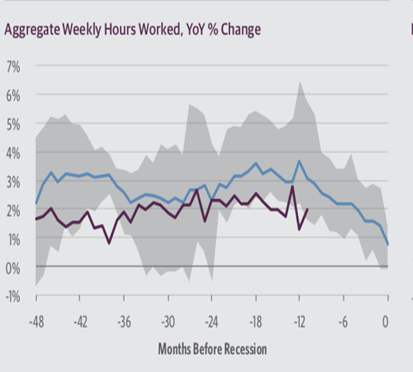
Weekly Hours Worked
The corporates increase spending in expectation of higher demands for product and services. This can increase the aggregate weekly hourly worked, if the increase in employment is not feasible. The aggregated weekly hours worked has experienced steep decline, in year on year change, recently. This indicates that the corporates have reduced their activity, and in worst scenario the inventory has touched the peak and it is decreasing in expectation of lower demand for their product or services.
A reduction in corporate activity to gauge lower demand will eventually lead to reduction in the economics growth and soon and eventually contribute to the recession.
RLeading Indicators
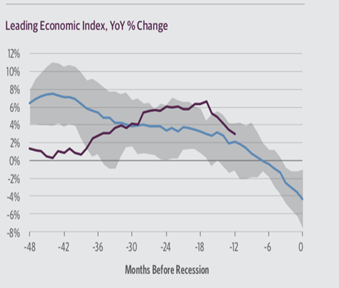
The leading economic index have deteriorated sharply in past 6 months.
Some of the other factors affecting the next recession are:
- Fiscal Deficit:
The fiscal deficit is high. Although the budget deficit is countercyclical, the extended period of expansion was different. The Government budget deficit rose to 4.5% from1 from 2.9% in 2014 as a percentage of GDP. This has been due to higher fiscal spending and lower tax rate to boost economy
Less space for rate cuts to boost economy activity and valuation of assets:
The recession would be prolonged relative to earlier recession. The average fed rate cuts during recession has be 5.5%. The Fed can move to others tools like Quantitative easing (QE), Japanese type yield curve control and negative short -term yield. The corporate debt has seen a sharp rise and the fed lacks the statutory ability to purchase corporate debt for quantitative easing, but who knows the desperation level of FED in next recession. None the less, the Fed has more purchasing power to boost economy relative to other central banks as Fed holds only 20% of GDP as its balance sheet, where Euro central bank and Japan hold 40% and 100% 3respectively.
- Global slowdown:
The world is experiencing a global slowdown and this would add to the concern of global slowdown of U.S. China provided credit easing and infrastructure spending in the 2008 crisis. It is unlikely to provide the same stimulus, even if it provides any, in the next recession.
Conclusion:
In the middle of slower global economic outlook and uncertainty regarding the Brexit, the data from US is indicating that the world’s largest economy is heading to a recession in a year to 18 moths from now.
The inverted 10 year – 3-month yield curve, dovish stance by Fed, deteriorating leading indicators and real retail sales, and reduction in the weekly hours’ worked growth rate are some of the signs towards a recession in the mid of 2020. The hope is that the severity of the recession will be less relative to recent recession, majorly due to stronger balance sheet of banks, but it will take longer time to heal as the monetary policy has less power to stimulate economy by reducing interest rates it has lower spread before reaching the zero-interest floor. The significant increase in corporate debt and the contribution of fiscal deficit to the extended period of business expansion has placed the credit market and fiscal policymaker with less tools to counter the recession“
with inputs from Ronak Chaturvedi