Macromania explains….It’s well-known that in the United States, recessions are often preceded by an inversion of the yield curve. Is there any economic rationale for why this should be the case?
Most yield curve analysis makes reference to nominal interest rates. Economic theory, however, stresses the relevance of real (inflation-adjusted) interest rates. (The distinction does not matter much for the U.S in recent decades, as inflation has remained low and stable). According to standard asset-pricing theory (which, unfortunately for present purposes, abstracts from liquidity premia), the real interest rate measures the rate at which consumption (a broad measure of material living standards) is expected to grow over a given horizon. A high 1-year yield signals that growth is expected to be high over a one-year horizon. A high 10-year yield signals that annual growth is expected, on average, to be high over a ten-year horizon. If the difference in the 10-year and 1-year yield is positive, then growth is expected to accelerate. If the difference is negative–i.e., if the real yield curve inverts–then growth is expected to decelerate.
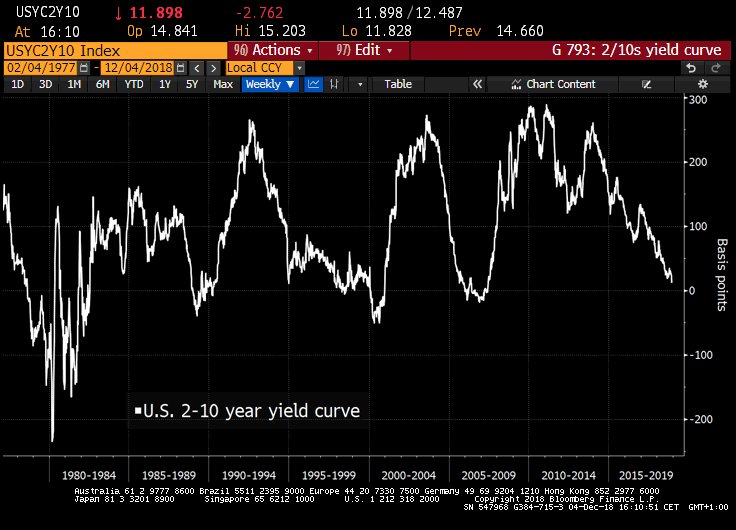
(Only 12bps to go. US 2s/10s yield curve drops to 12bps, lowest since 2007.)
What is the economic intuition for these claims? One way to think about this is in terms of Friedman’s Permanent Income Hypothesis, which states that an individual’s desired consumption expenditure today should depend not only on current income, but the likely path of his/her income over the foreseeable future. The logic of this argument follows from the assumption that people are willing and able to smooth their consumption over time, given their expectations over how their incomes are likely to evolve over time. For example, if people expect their income to be higher in the future, then they will want to consume more today in order to smooth out their consumption. They can attempt to do so by saving less (or borrowing more). If a community is collectively “bullish” in this sense, desired consumer spending should rise in the aggregate, and desired saving should fall, leading to upward pressure on the real interest rate.
Alternatively, suppose that firms suddenly turn bullish on the likely returns to capital spending. Then the resulting increase in the demand for investment financing should drive real interest rates upward. In this case as well, a higher real interest rate signals the expectation of a higher rate of economic growth. If individual expectations over future prospects are correct more often they are incorrect, then higher real interest rates today should be correlated with higher future growth rates.
So, in theory at least, an inverted yield curve does not forecast recessions–it forecasts growth slowdowns. Nevertheless, there is a sense in which an inverted (or even flat) yield curve can, in some circumstances, suggest that recession is more likely. Here’s the basic idea.
Consider an economy that grows over time, but where growth occurs unevenly (i.e., the economy alternates between high- and low-growth regimes). Imagine, as well, that the economy is occasionally buffeted by negative “shocks”—adverse events that occur at unpredictable moments in time (an oil price spike, a stock market collapse, etc.). It seems clear enough that in such an economy, recessions are more likely to occur when a shock of a given size occurs in a low-growth state as opposed to a high-growth state.
Now, as explained above, suppose that an inverted yield curve forecasts a deceleration in growth. Then the deceleration will entail moving from a higher growth state to lower growth state. Suppose this lower growth state is near zero. In this state, growth is now more likely to turn negative in the event of a shock. In this way, an inverted yield curve does not forecast recession; instead, it forecasts the economic conditions that make recession more likely.
My two cents
I think something is triggered when yield curves invert, or some recessionary force triggers an inverted yield curve,or maybe the answer is so simple as central banks will raise rates until they cause a recession. The graph above suggests US Federal Reserve would do well to stop raising rates now and see what happens. They seem on course to repeat the previous cycles. The elephant in the room this time is US fiscal deficit which is set to touch a trillion in a year and if US were to attract worlds saving to fund this deficit then they need higher rates and that complicates the picture.